Nouns
Nouns refer to persons, animals, places, things, or ideas. Nouns encompass most words used in the English vocabulary, and there are several different types of nouns, including common nouns, proper nouns, concrete nouns, abstract nouns, and collective nouns. It is important to understand how types of nouns are formed since different rules apply to different noun types.
Types of nouns
| Noun Type | What it does | Noun examples |
|---|---|---|
| Common noun |
Refers to people or things in general |
man, sister, frog, day, city |
| Proper noun |
Refers to names of a particular person, place, organization, or thing |
Apple, Paris, Microsoft, Mary, Amazon, St. James Samsung |
| Concrete noun |
Refers to physical things that one can touch, see, hear, smell, or taste |
balloon, board, chocolate, laptop, pumpkin, shoulder |
| Abstract noun |
Refers to non-physical and intangible things |
beauty, bravery, love, time, friendship, fear, hatred, honesty |
| Collective noun |
Refers to a group of things, people, or animals, etc. |
committee, group, flock, herd, bunch, pack, fleet, set |
Common Nouns vs. Proper Nouns
Proper nouns differ from common nouns in that proper nouns refer to specific names of a person, place, or thing. Proper nouns always begin with a capital letter.
- Common noun
- Have you seen my cat?
- Proper noun
- Have you seen my cat, Fluffy?
- Common noun
- I visited another country for spring break.
- Proper noun
- I visited France for spring break.
Types of Common Nouns
Common nouns are words used to denote general items. There are three types of common nouns: concrete nouns, abstract nouns, and collective nouns.
Concrete nouns
Concrete nouns are physical things that can be identified through one of the five senses (taste, touch, sight, hearing, or smell).
- Example
- I love the flower you gave me.
- Example
- The liquid was boiled in a flask at 110 degrees.
Abstract nouns
Abstract nouns are non-physical things that cannot be identified through one of the five senses (taste, touch, sight, hearing, or smell). Generally, it refers to ideas, qualities, and conditions.
- Example
- Many people say that time is relative.
- Example
- Try to find the beauty in things around you.
Collective nouns
Collective nouns are words that represent a group of people, animals, or things. Collective nouns can be either plural or singular. However, it is more common to use collective nouns as singular nouns.
- Example
- The choir at the church is really good.
- Example
- I saw a flock of birds flying.
Nouns as Subjects
All sentences should have a subject (person, place, or thing that performs the action), and the subjects in sentences are always nouns or pronouns.
- Example
- Research papers are very important to scientific studies.
- Example
- Susan works as the COO of the company.
Nouns as Objects
Nouns can be used as objects in sentences, both direct objects and indirect objects.
Direct objects
The direct object of a verb is the thing being acted upon. The direct object can be located by finding the verb and asking, “What or whom is being impacted?
- Example
- The little girl loves her nanny.
(The girl loves whom? Her nanny)
- Example
- The university president awarded the best students.
(Whom did the university president award? The best students.)
Indirect objects
The indirect object is the recipient or beneficiary of the action. The indirect object can be located by finding the verb and asking, “For whom or to whom is this action directed?”
- Example
- In art class, I made my sister a sculpture.
(I made what? A sculpture. For whom? My sister)
- Example
- Let’s bring our parents breakfast in bed.
(Let’s bring what? Breakfast in bed. To whom will we bring it? Our parents.)
Get professional proofreading and expert feedback on any document!
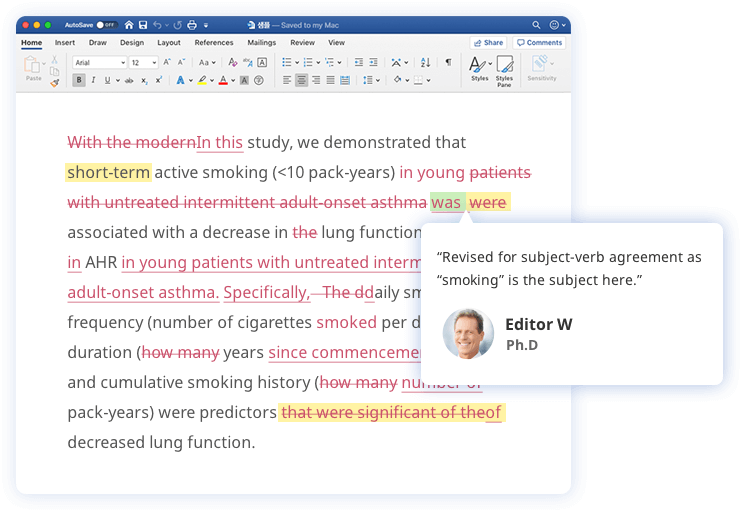
- Academic papers
- Admissions essays
- CVs/resumes
- Business reports
- Blog and website content
- Personal essays
Subject and Object Complements
Subject complements
Subject complements are words or phrases that follow a linking verb (a verb used to link a subject to a new identity or description) and identify or describe the subject.
- Example
- She looks like a ghost.
- Example
- Lions and tigers are mammals.
Object complements
Object complements follow a direct object to rename it or state what it has become.
- Example
- She was named the captain of the team.
- Example
- Her mother will do anything to make her a doctor.
Nouns as Modifiers
Nouns can be placed before other nouns to describe a particular type of person or thing. In this case, two nouns are placed side by side and the noun placed before another noun functions as an adjective in that it is added to further describe the other noun.
- Example
-
chocolate cake
a fifty-kilometer journey
leather purse
Appositives
An appositive is a noun or noun phrase that renames or clarifies the noun preceding it. It serves the purpose of adding information about another noun. The two nouns are separated by a comma.
- Example
- I have to call my friend, Bill, about the problem.
- Example
- My car, a small sedan, is not big enough to fit all of you.
Countable vs. Uncountable Nouns
Countable nouns
Countable nouns are individual people, animals, places, things, or ideas which can be counted.
- Example
- The calculus book is on the table.
- Example
- There are at least twenty French restaurants on this street.
Uncountable nouns
Uncountable nouns are not individual objects, so they cannot be counted. Uncountable nouns can be paired with words expressing plural concepts (glass, flock, pair) or quantifiers (some, many, a lot of).
- Example
- There is no more water in the cup.
- Example
- Her level of intelligence is extremely high.
- Incorrect
- Can I have a bread?
- Correct
- Can I have a loaf of bread?
- Incorrect
- The vase is made of a clay.
- Correct
- The vase is made of clay.
- Incorrect
- Put in two butter to make the cupcake.
- Correct
- Put in two scoops of butter to make the cupcake.
Possessive Nouns
Possessive nouns are nouns that possess something--the noun is the possessor of a thing or quality. Typically, possessive nouns are formed by adding apostrophes and an “s” to the noun. For possessives of nouns that are plural or end in “s,” only an apostrophe is added.
- Example
-
the laundry's smell
a tree's beauty
cabbage’s nutrition








