Sentence Structure (Word Order Rules)
A sentence is a group of words that expresses a complete thought and contains a subject and a predicate. The most basic sentence structure consists of only one clause. However, many sentences have one main clause and one or more subordinate clauses.
The standard order of words in an English sentence is subject + verb + object. While this sounds simple, it may be difficult to identify the subject(s), verb(s), and object(s), depending on the structure and complexity of the sentence. There are four types of sentence structure: (1) simple, (2) compound, (3) complex, and (4) compound-complex.
Types of sentence structures
| Sentence structure type | Sentence parts | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Simple Sentence |
Independent clause |
I like animals. |
| Compound Sentence |
Independent clause + coordinating conjunction (or semicolon) + independent clause |
I like animals, but Molly prefers plants. |
| Complex Sentence |
Independent clause + subordinating conjunction (or relative pronoun) + dependent clause |
I like animals because they are cute. |
| Compound-Complex Sentence |
Independent clause + subordinating conjunction + dependent clause + coordinating conjunction + independent clause |
I like animals because they are cute, so I work at an animal shelter. |
Table of Contents
Sentence Structures in Academic Writing
Simple Sentence Structure
A simple sentence is the most basic sentence structure and consists of a single independent clause.
Types of clauses
An independent clause expresses a full thought. Only independent clauses can function as complete sentences.
- Example
- The proposed system has the advantage of a wide scope.
I went shopping last weekend.
The cat is sleeping by the window.
In contrast, a dependent clause does not express a full thought and cannot function as a complete sentence.
- Example
- which was developed over three months
even though I was tired
because the weather is sunny
A dependent clause starts with either a relative pronoun or subordinating conjunction.
Common subordinating conjunctions
because, since, once, although, if, until, unless, why, while, whether, than, that, in order to
Common relative pronouns
that, which, who, whom, whoever, whomever
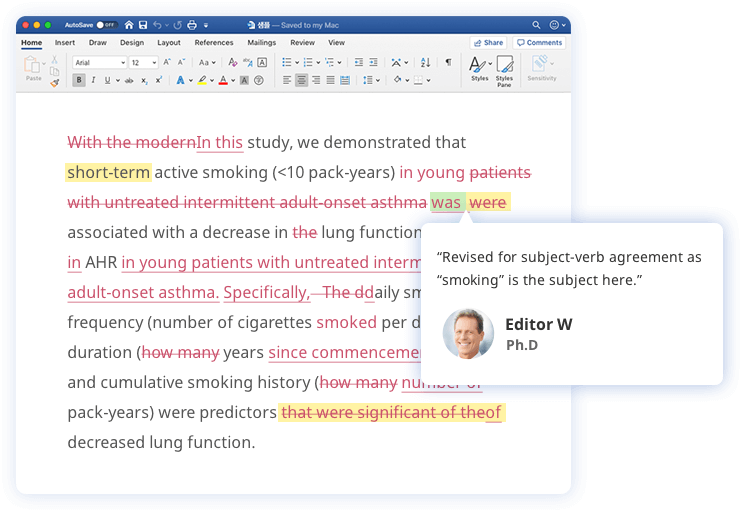
Subject of a sentence
The subject is whatever is performing the action of the sentence. This is the first of the two basic components of a sentence.
- Example
- This study investigated the relationship between the personal traits and clinical parameters.
- Example
- Dolly made a cake for the party.
Predicate of a sentence
The predicate contains the verb (the action) and can include further clarifying information.
- Example
- This study investigated the relationship between the personal traits and clinical parameters.
- Example
- Mary gave her sheep a bath.
Direct and Indirect Objects
The direct object is the person, thing, or idea that receives an action.
- Example
- This study investigated the relationship between the personal traits and clinical parameters.
- Example
- Dolly made a cake.
The indirect object is the person, thing, or idea for which an action is being done.
- Example
- The national lab offered us an opportunity to work on an exciting new project.
- Example
- Mary gave her sheep a bath.
Transitive vs. Intransitive Verbs
A transitive verb is the action the subject takes on a direct object.
- Example
- We fabricated a composite.
Here, “we” is the subject, “fabricated” is the transitive verb, and “a composite” is the direct object.
An intransitive verb is a verb that does not have to be followed by an object. Intransitive verbs can function as predicates all on their own.
- Example
- We arrived.
We arrived early.
- Example
- I always eat.
I always eat before work.
“We” and “I” are the subjects; “arrived” and “eat” are intransitive verbs.
Subject Complement
A subject complement complements the subject by renaming or describing it. Subject complements always follow a linking verb, which is often a form of the verb “to be.”
- Example
- The material is a gold composite.
“Gold composite” renames the subject “the material.”
- Example
- Charlotte is very pretty.
“Pretty” describes the subject “Charlotte.”
Get professional proofreading and expert feedback on any document!
- Academic papers
- Admissions essays
- CVs/resumes
- Business reports
- Blog and website content
- Personal essays
Compound Sentence Structure
A compound sentence is composed of two or more independent clauses connected by a coordinating conjunction or semicolon. Note that US English conventions dictate that coordinating conjunctions must be used with a comma when joining independent clauses.
Structure of a Compound Sentence: Independent clause + coordinating conjunction (or semicolon) + independent clause
List of coordinating conjunctions: and, but, yet, or, nor, for, so
- Example
- The material is a gold composite, and it was fabricated in clean room no. 45.
- Example
- Glenda usually eats before work, but today she could not.
- Example
- The proposed system has the advantage of a wide scope; it uses a novel algorithm that expands the range by a factor of ten.
Complex Sentence Structure
A complex sentence is composed of an independent clause and a dependent clause.
Structure of a Complex Sentence: Independent clause + subordinating conjunction (or relative pronoun) + dependent clause
- Example
- We built a new system because the previous model had to be narrowed in scope.
- Example
- Sarah will buy a train ticket if her flight is cancelled.
Compound-Complex Sentence Structure
A compound-complex sentence is composed of two or more independent clauses and one or more dependent clauses.
Structure of a Compound-Complex Sentence: Independent clause + subordinating conjunction + dependent clause + coordinating conjunction + independent clause
- Example
- The first method failed because it caused the wires to melt, but the second method succeeded in bending the wires without causing the same issue.
- Example
- Sarah’s flight took off before she started driving to the airport, so she drove to the train station instead.








